Everything you need to know about home insulation
Did you know that insulation is one of the best ways to make your home more energy efficient? In fact, it can save you up to 30% on your energy bills. If you’re thinking about adding insulation to your home, or if you’re just curious about what it is and how it works, read on. We’ll explain everything you need to know about home insulation.
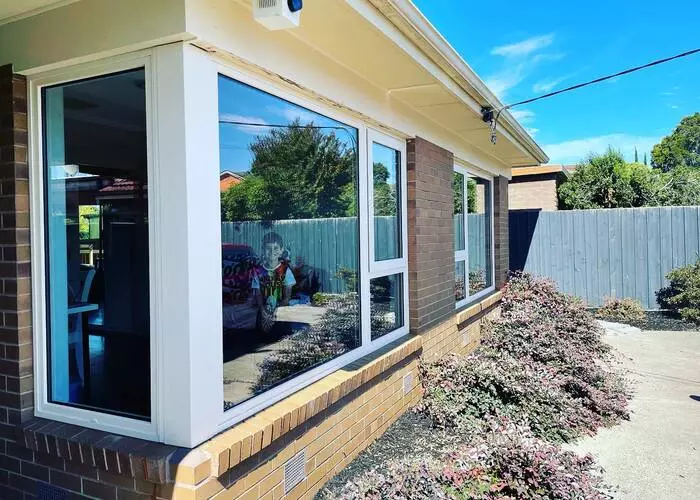
Why use uPVC window frames and doors?
Insulation

Soundrproofing
The best thing about UPVC windows and doors are their noise reducing properties. These materials work in combination with double glazed paneling to help decrease outside sounds passing through your home by up 50%.
Weather Resistant
UPVC windows and doors are a great choice for those who want their property to last longer than natural materials such as wood. They don’t react with water or air, meaning that these exterior installations will never have an issue of weathering-they can withstand anything!
Ventilation
UPVC windows are a great way to provide ventilation in your home. They come with different styles and configuration options that allow you more control over how much air comes into each room, as well as where it goes when outside noise becomes distracting or hot inside without having any drafty spots on open floors near doors leading out from rooms
Fire Retardant
Aluminium vs. uPVC
The importance of roof insulation
On top of that, efficient insulation reduces CO2 emissions which aids in combating air pollution.
There are two types of roof insulation:
Warm insulation
Cold insulation
Two important factors to consider with home insulation
In the context of home insulation, “air filtration” refers to how much the air gets through. This is not specifically referring to the use of a standard air duct filter, but rather having the ability to control how much air passes through.
The insulation needs to “breathe” to do its job, so there must be a flow of air to the outside surfaces of the insulation. Insulation also needs to be sealed off on the inside surfaces. Walls or ceilings should be lined with a vapor barrier, a layer of a watertight material. Insulation is technically a solid with a lot of air in it therefore, it is not an air gap. You must have nothing in the air gap except air itself. So, if you’re installing under a roof or in a wall, you must create an air gap.
SHGC
Solar Heat Gain Control refers to how much of the sun gets through.
SHGC and U-factor can be decreased in the glass component of a window assembly in multiple ways: Low-emissivity (low-e) coatings can reduce the ultraviolet and infrared light that passes through the glass, limiting heat gain while preserving visible light transmission.
What is a “passive house”?
Passive House certification is an international standard that provides the most energy-efficient building technologies to reduce CO2 emissions. There are three levels of Passive Houses: Classic, Plus and Premium which differ based on how much efficiency they need to achieve their goal.
Classic does not require installation of renewable energies.
Plus needs them for maximum performance.
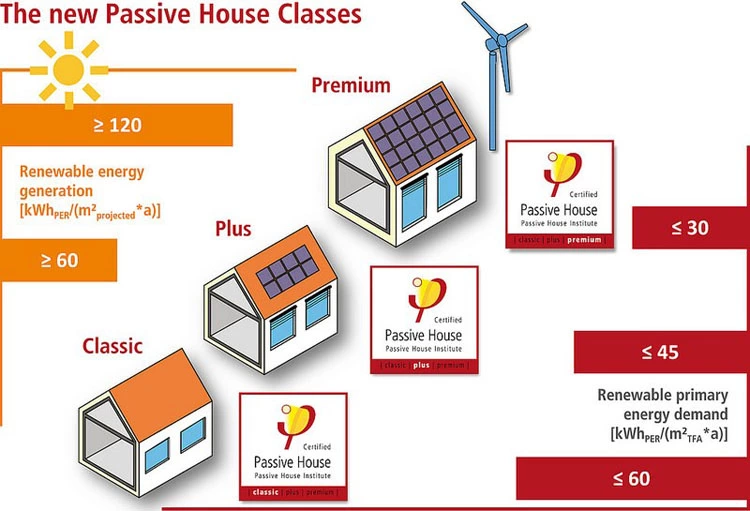
Source: Passive House Institute
Source: Passive House Institute
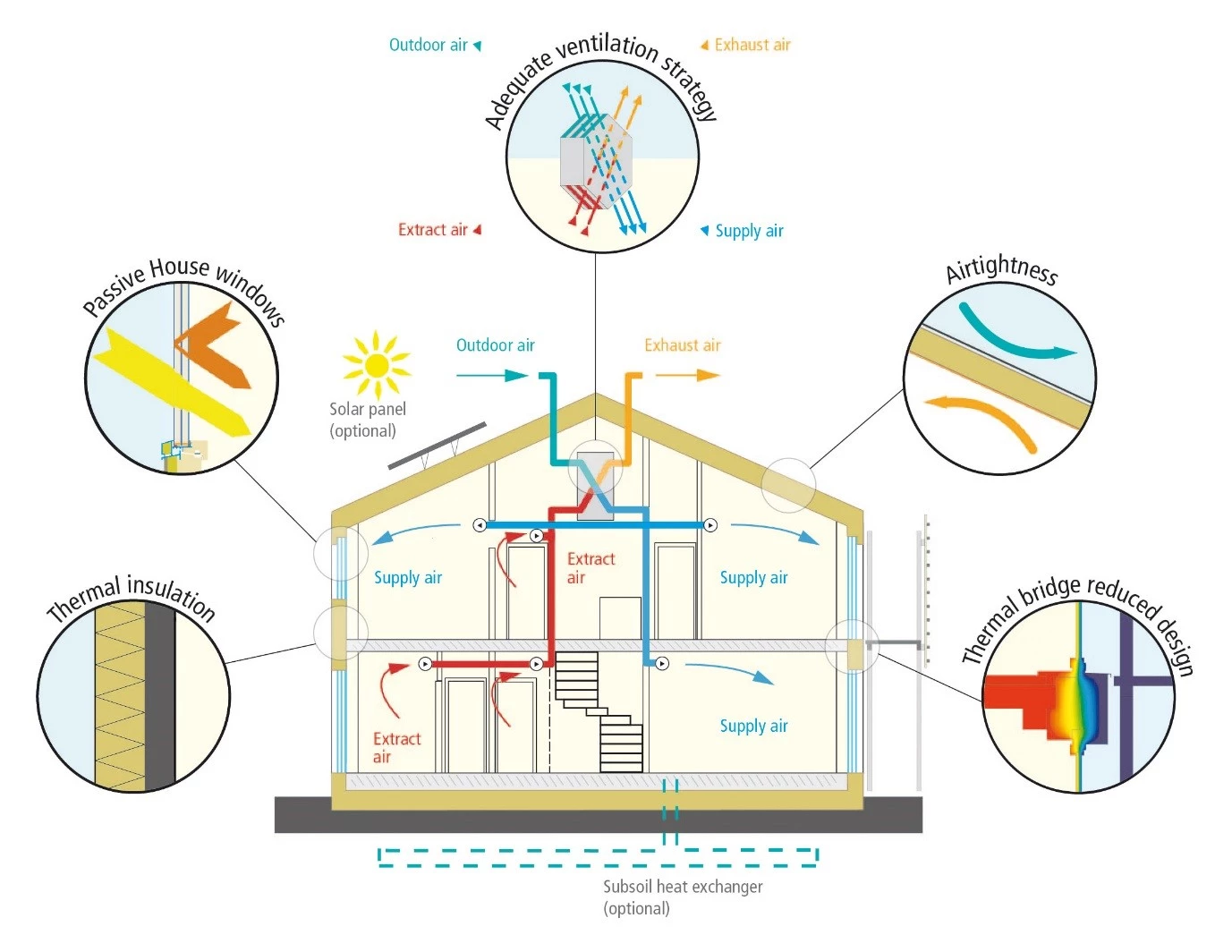
The Passive House must be airtight to control water vapour transfer and the internal quality. This prevents uncontrolled infiltration through walls, roof or floor which can draw pollutants inside houses, causing moisture damage .
The Passive House was originally designed to be an airtight building that requires ventilation. While it can naturally vent, most people will need some sort of mechanical system with heat recovery in order for the space not feel stuffy or too warm during cold months when windows are closed and there’s no outdoor airflow coming into a room through which you could breath easily without opening them up at night time (for example winter nights).
Conclusion
uPVC insulation is a great way to make your home more energy efficient. In fact, when coupled with uPVC window frames and doors, it can be even more effective in keeping your home at a comfortable temperature.
If you’re interested in learning more about how uPVC insulation can benefit you, reach out to our experts! We would be happy to discuss the options available and help you choose the best solution for your needs. Thanks for reading!


